The Battle of Kars: A Clash of Empires
The Battle of Kars unfolded on August 19, 1745, serving as the conclusive engagement in the Ottoman-Persian War, positioned in northeastern Turkey. It marked the culmination of a series of victories that compelled the Ottomans to enter negotiations under challenging circumstances. Following their successive military defeats, the Ottomans found themselves without the means to exert control over the Persians through military force. Despite this, Nader Shah, the Persian ruler, opted not to launch a counter invasion of the Ottoman Empire. Instead, he pursued a diplomatic resolution to bring an end to the hostilities. Diplomats engaged in discussions, leading to the signing of the Treaty of Kerden, effectively concluding the Ottoman-Persian War of 1743-1746.
 |
| Image Source: Google, Image By: World History |
Empirical Legacies: Ottoman and Persian Tales of Power
To grasp the dynamics of the Ottoman vs Persian War, it is crucial to delve into the historical context of both empires. The Ottoman Empire, established in the 13th century by Osman I, emerged as a formidable force during the 15th century under the leadership of Mehmed the Conqueror. Spanning vast territories across Europe, Asia, and Africa, the Ottoman Empire evolved into a significant global power. On the other hand, the Persian Empire, also known as the Safavid Empire, ascended to prominence in the 16th century under the rule of Shah Ismail I. Renowned for its diverse ethnic heritage and its sway over a substantial portion of the Middle East, the Persian Empire stood as a notable force in the region.
 |
| Image Source: Google, Image By: Flickr |
Regional Rivalry: Ottoman and Persian Quests for Dominance
Various factors contributed to the outbreak of the Ottoman vs Persian War. One primary cause stemmed from the regional ambitions of both empires. The Ottomans and the Persians were driven by the desire to expand their territories and exert influence over the surrounding regions. Religious differences added fuel to the conflict, with the Ottomans predominantly being Sunni Muslims and the Persians primarily adhering to Shia Islam. This religious divide heightened tensions as both empires sought to promote their respective sects and establish religious supremacy.
Another crucial factor that led to the war was the competition for control over strategic trade routes. The Ottoman Empire held sway over key trade routes, including the Silk Road connecting Asia to Europe. The Persians aimed to assert their dominance over these vital trade routes, intensifying the rivalry between the two empires and amplifying the conflict over trade and commerce.
Centuries of Strife: Ottoman-Persian Battles Unveiled
The Ottoman-Persian Battles constitute a series of conflicts spanning several centuries between the Ottoman Empire and various Persian states. One significant encounter within this historical tapestry was the Battle of Chaldiran in 1514. Here, the Ottomans, commanded by Sultan Selim I, clashed with the Persians under the leadership of Shah Ismail I. The Ottomans emerged victorious, solidifying their control over eastern Anatolia and dealing a blow to the Persian Empire.
 |
| Image Source: Google, Image By: Wikimedia Commons |
Another notable chapter unfolded with the Siege of Baghdad in 1638. Sultan Murad IV led the Ottoman forces in a prolonged siege against the Persian-held city of Baghdad. Despite facing intense resistance, the Ottomans ultimately succeeded in capturing the city, marking a pivotal moment in the ongoing conflict.
The Battle of Kars in 1745 stands out as the concluding major conflict in the Ottoman-Persian Wars. In this engagement, Nader Shah's forces triumphed over the Ottoman army, prompting negotiations that highlighted the Ottomans' weakened position in the aftermath of the defeat.
Empire Transformations: Ottoman Ascendancy in the Middle East
The Ottoman vs Persian War exerted a profound influence on the region, leaving a lasting impact both during and after the conflicts. One immediate consequence was the reconfiguration of territorial boundaries. The wars resulted in significant territorial expansions for the Ottomans, as they extended their empire into Persian-held territories, thereby shaping the enduring political landscape of the Middle East.
Furthermore, these conflicts precipitated the decline of the Persian Empire and the ascendancy of the Ottoman Empire as the predominant force in the region. The Ottomans emerged as a formidable power, wielding influence over vast territories and establishing themselves as the foremost Islamic empire in the area.
Culturally, the wars played a pivotal role. The religious divide between the Sunni Ottomans and the Shia Persians deepened, expanding the existing religious split in the region. This sectarian divide continues to shape the political and social dynamics of the Middle East, leaving a lasting cultural legacy.
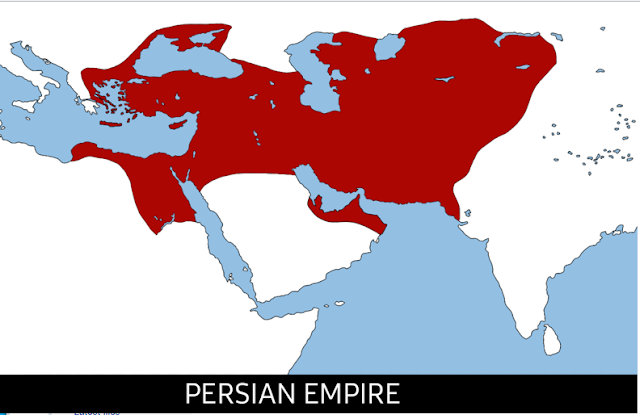 |
| Image Source: Google, Image By: Wiki Media Commons |
Ottoman Dominance: Political Legacy of the Wars
The Ottoman vs Persian Wars had comprehensive effects on cultural, political, and economic dimensions. These conflicts facilitated the exchange of ideas, art, and literature between the two empires, enriching the cultural and intellectual landscapes of both societies. However, the war also brought about the destruction of traditional sites and the displacement of populations, leaving enduring impacts on the region's cultural fabric.
In terms of politics, the wars solidified the Ottoman Empire's dominance over the Middle East. The Ottomans implemented a centralized system of governance and introduced administrative reforms that would shape the political structure of the region for centuries.
Economically, the wars disrupted trade routes, leading to a redirection of commerce. The Ottoman Empire's control over crucial trade routes enabled them to dominate trade and amass wealth. This economic mechanism further bolstered their influence in the region, establishing a lasting economic legacy.
Geopolitical Echoes: Ottoman vs Persian Wars in Today's World
The enduring legacy of the Ottoman vs Persian Wars persists in contemporary times, as the territorial borders established during the conflict continue to influence the geopolitical landscape of the Middle East. The religious divide between Sunni and Shia Islam, heightened during the war, remains a significant factor shaping the region's dynamics today.
The Ottoman vs Persian War has captured the imagination of writers, historians, filmmakers, and artists across various epochs. It has been a recurring theme in popular culture and media, depicted in forms ranging from epic poems to historical novels. The conflict has served as a source of inspiration and motivation for creative works, bringing the historical events to life for a broader audience through films and television series.
 |
| Image Source: Google, Image By: Wikimedia Commons |
Conclusion:
The Ottoman vs Persian Wars were pivotal events that shaped the history of the Middle East, leaving a profound impact on the region's political, cultural, and economic landscape. The legacy of these wars endures in contemporary times, influencing the geopolitical dynamics of the Middle East. The portrayal of these conflicts in popular culture and media remains a compelling subject that captures the attention of readers worldwide. Exploring the intricacies of these historical conflicts offers valuable insights into the complexities of the Middle East and its rich history.





